Internal links are a key part an overall SEO strategy. To give an analogy, internal links can be likened to a roadmap within a city. Just as a roadmap helps people navigate through a city by providing clear directions and connecting different locations, internal links guide search engines to navigate and understand the structure of a website. They also help users discover different pages on the website that are linked together with a logical flow.
This blog will explain what internal linking is, the role internal links play in an overall SEO strategy and some best practices you should consider when adding them into your own site.
Table of Contents
What are Internal Links?
In the world of SEO, internal links are an essential element that can significantly impact a website’s performance. Internal links are hyperlinks that connect one page of a website to another page within the same domain. They are called “internal” because they point to different pages within the same website, as opposed to “external” links that connect to pages on a different domain.
Internal links are used for navigation purposes, helping users easily move from one page to another within a website. They also help search engines understand the structure and hierarchy of a website, which can have a positive impact on SEO.
Difference between Internal and External Links
While both internal and external links are important for SEO, they serve different purposes. As mentioned earlier, internal links connect pages within the same website, while external links connect to pages on different websites.
The main difference between internal and external links is that internal links are under the control of website owners, allowing them to optimise their website’s internal linking structure. On the other hand, external links are not within the website owner’s control and are dependent on other websites linking back to their content.
Whilst internal links help to create content clusters within a site by linking together related content to form topic hubs, external links help to build URL and overall domain authority by passing on authority from the linking domain. Once an external link is built to a page, the internal linking structure allows this authority to be shared throughout the content cluster and rest of the site, which is why it is essential you have a solid internal linking structure to compliment your external link building efforts.
Although this blog is focused on internal linking, we do have another guide on the basics of link building which focuses on external linking that you should check out for more information on that!
Why are Internal Links Important for SEO?
Internal links play a crucial role in improving SEO for several reasons. Not only do internal links help users to move through your site on their journey to purchase, but they also help Google to understand the structure and purpose of your site and its different sections. The benefits offered by having a strong internal linking structure include:
Improved Website Navigation
Internal links help users easily navigate through different pages of a website, making it more user-friendly. When users can easily find and access relevant content, it increases their engagement and reduces bounce rates, which can positively impact SEO.
Spreading Link Equity
Internal links allow website owners to distribute link equity (also known as link juice) across different pages of their website. When one page links to another, it passes on some of its authority to the linked page, helping it rank better in search results. As mentioned earlier, this is even more important when there are external links pointing to certain pages on site, and internal links helps to share out this authority.
Establishing Website Hierarchy
Internal links help establish the hierarchy and structure of a website. They create a logical flow from the homepage to other pages, indicating which pages are most important and relevant. This helps search engines understand the website’s structure and improves their ability to crawl and index the site, prioritising resource for your most important pages.
Increasing Page Authority
Internal links can help boost the authority of individual pages within a website. When a page receives multiple internal links from other relevant pages, it signals to search engines that the page is valuable and authoritative, as you seemingly want users to be able to find it, leading to improved rankings.
Enhancing Keyword Relevance
Internal links with relevant anchor text (the clickable text of a hyperlink) can help search engines understand the content of the linked page. The anchor text basically tells the user and Google what topic the linked page is going to be about. This can improve the keyword relevance of the linked page, which in turn can improve its rankings for those keywords.
Establish Relationships Between Pages:
Internal links within the content of pages help to indicate their relationship to one another. A parent page should include links to all subcategory pages, and the individual subcategory pages should all include links back to the main parent page to form a content cluster. To add to this, each of these pages should internally link to related blog content that will help answer related questions around the category, to position you as an authority on the topic overall.
How to Build Internal Links for SEO?
Building effective internal links requires careful planning and strategy. To get the most out of your internal linking structure, you should plan it out with the end user in mind:
- Where do you want them to go?
- What will aid their customer journey to purchase?
- What makes sense to link to from a user point of view?
- Which pages are the most closely related?
We have outlined below the steps to take when planning out a new internal linking strategy.
Plan out your overall site architecture
When thinking about your internal linking plan, you need to keep in mind your overall site hierarchy, so you know which pages to link to and where. If you’re building a new site from scratch, you can do this by scribbling out a hierarchy diagram with pen and paper to outline:
- Top level pages
- Subcategory pages
- Blog pages and categories
- Other pages required – e.g. Contact Page, About Us
Once you know which pages you have, you can start to think about how you can link them all together.
Create/review your navigation and footer
From the above step, you will have established which pages are your most important top-level pages that you want a user to be able to navigate to from any page on your site. These are the pages that should be linked to within templated sections, such as your main navigation and footer.
A link from the main navigation is incredibly powerful for SEO and indicates the page is very important, therefore Google is likely to crawl and index the page faster, and more often. This is because a link from the main navigation means there is a link to the page on ever other page across the website.
Main navigation links should include all of your main product or service category pages. For larger e-commerce sites, a mega menu will be required to keep this clean for users to understand.
Likewise, footer links will also appear across every page on your site, so this should be filled with useful pages to users that don’t fit within your main navigation. This includes pages such as delivery and returns information, as well as privacy policies.
Add quick links to your top level pages
Within the top-level category pages, links should be added to related sub-category pages. This can be done through standard in-text links, but to make them easier for users to see, you can use quick link buttons.
An example of this can be seen on Sigma Sports’ website where they link to individual bike families from the main brand page:
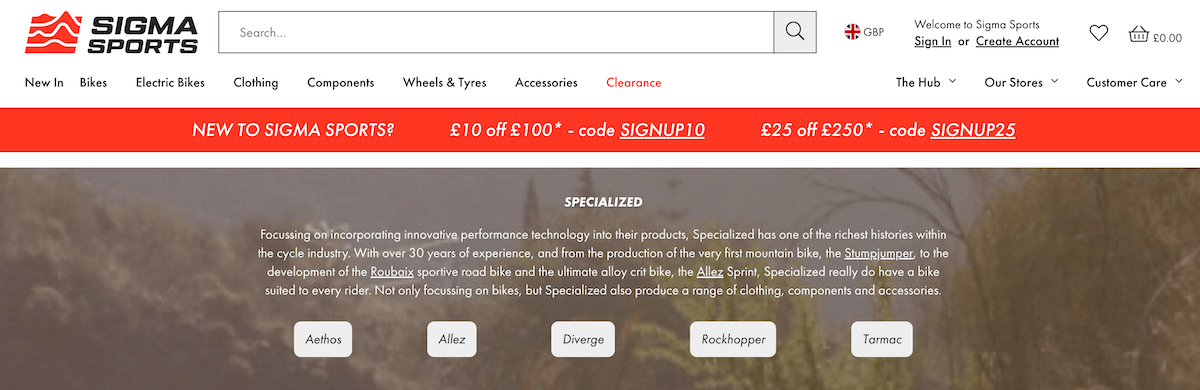
For an ecommerce site, you can plan out these quick links by thinking about how users generally filter your top-level page. If it is a clothes shop and we’re talking about the category “Dresses”, the quick links would likely be the different styles of dresses that users would be looking for – e.g. Bodycon, Midi, Maxi etc.
Add text links into your content
Once you’ve planned out all of the templated links, you can add more links within pages using text content on the page. This is a good way to link blogs to their related category pages. Using relevant anchor text that already appears naturally within the blog, you can link to the main category or service page the blog is aimed at providing information around.
In the example below, you can see how our blog on “How long does SEO take to work?” includes an in-text link within the body of the text pointing to the main SEO service page.
Internal Linking Best Practices
When building internal links on your site, here are some best practices you should keep in mind for internal linking that can help you optimise your website as well as possible for SEO success:
Create High-Quality Cluster Content
The first step in building internal links is to create high-quality, relevant content that is valuable to users and fully explains your products/services. When you have valuable content in other pages on your website, you are more likely to link to it from your main pages to aid the user journey.
Use Descriptive Anchor Text
Anchor text is the clickable text of a hyperlink. When creating internal links, use descriptive anchor text that clearly indicates the content of the linked page to help with keyword rankings. Avoid generic anchor text like “click here” or “read more” as they provide little context to search engines and users.
Link to Relevant Pages
When creating internal links, make sure to link to relevant pages that are related to the content of the current page. This helps search engines understand the context of the linked page and improves the user experience by providing additional relevant information.
Follow a Logical Linking Structure
Create a logical linking structure that establishes a hierarchy and flow from the homepage to other pages of your website. This helps search engines understand your overall site architecture.
Prioritise Contextual Links
Contextual links are links placed within the body of the content, surrounded by relevant text. These types of links are more effective than footer or sidebar links as they are more prominent and provide contextual relevance to the linked page.
Keep it Natural and User-Friendly
Internal links should be placed in a way that makes sense to users and adds value to their browsing experience. Avoid over-optimisation and excessive linking, as it can be seen as spammy by search engines and may result in penalties.
Link to High-Quality and Relevant Pages
When creating internal links, it’s important to link to high-quality and relevant pages that provide additional value to users. Avoid linking to low-quality or irrelevant pages, as it can negatively impact the user experience and SEO.
Utilise Categories and Tags
Categories and tags are used to organise content on a website. They can be leveraged for internal linking by linking to category or tag archive pages, which can help users navigate to related content and improve the overall website structure.
Monitor and Update Internal Links Regularly
As your website grows and evolves, it’s crucial to regularly monitor and update internal links to ensure they are still relevant and functional. Broken or outdated links can negatively impact user experience and SEO, so make sure to fix them promptly.
As you can see, when done correctly, internal linking can help to improve your website’s visibility in search results by enhancing the overall user experience. By following the best practices outlined above, you can optimise your internal linking strategy and drive more organic search traffic to your website.
If you need help getting started with your internal linking review, get in touch and let our SEO experts help you.






